Harvard Students Create Controversial Meta Smart Glasses App That Exposes Sensitive Personal Details
In a world that’s becoming increasingly technological, innovations are changing the way we interact with our surroundings and with one another. One such innovation is the recently developed application by a group of Harvard students in tandem with Meta’s smart glasses that will reveal personal details about an individual in real-time. As amazing as this application is, it spawns great controversy regarding its invasion of privacy and ethical violations.
In a world that’s becoming increasingly technological, innovations are changing the way we interact with our surroundings and with one another. One such innovation is the recently developed application by a group of Harvard students in tandem with Meta’s smart glasses that will reveal personal details about an individual in real-time. As amazing as this application is, it spawns great controversy regarding its invasion of privacy and ethical violations.
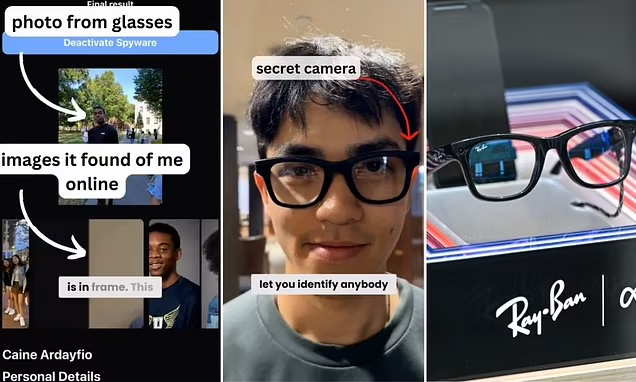
The Meta Smart Glasses is an application used with the smart glasses.
Already developed by ambitious group of Harvard students, it is put together to work completely seamless with Meta’s smart glasses. These are an AR wearable that overlays digital information over the real world. It makes use of advanced facial recognition and sophisticated data-mining technologies. It shows sensitive details about people in the user’s field of vision including their social media profiles, job information, even contact details and past interactions with third parties.
In a glance, these smart glasses will have all the details about every person the wearer may cross. Sounds like some sci-fi nonsense, but this technology is too real, and the fantastic innovation that presents so much great and risk has already entered public discourse with its attendant risks.
How Does It Work?
This app functions as an integrated combination of AI and machine learning combined with publicly available data. Here is a very condensed explanation of how the technology works:
Facial recognition: The smart glasses contain cameras that scan all the faces around the user. Using facial recognition software, the app can match those faces with images on social media sites or online.
Data aggregation: Whenever a person is identified through the application, it retrieves publicly available information of that person by aggregating from other online sources like social media profiles, professional profiles on LinkedIn, and so on.
Data Overlay in Real-Time: This data will be overlaid in real-time on the screen of the user’s smart glasses. This may include, among other things, name, job, interests, or even more sensitive information as far as it is available in the public domain.
The Privacy and Ethical Concerns
The technology behind the app is undoubtedly marvelous, but there are some serious concerns regarding privacy and ethics. It does bring up several pretty critical questions concerning consent and the right to privacy in public spaces-the concept of access to personal details about strangers instantly.
Lack of Consent
The most serious concern is that individuals going for scans will not control their information being disclosed. Generally, explicit consent must be obtained before information about people is released to the public or on public view. This gives rise to the fundamental issues of how people’s information will be used and if people have rights to opt out of information exposure.
Security Risks
The app would reveal all its sensitive information to the public, making it a tool for malicious actors. For example, if some person’s contact or location details are provided without their consent, they may end up being harassed or stalked. Identity theft, security breaches, and other risks may also come about from this data falling into the wrong hands.
Ethical Issues
Although the legal issues present themselves first, they are accompanied by wider moral questions surrounding surveillance and the intimacy of private information. Data privacy has long been the greatest subject of controversy; this app blurs lines between public information and private information, thus motivating a review of how much of our personal data should be offered to other people and even strangers without our knowledge and consent.
Legal Implications
The legal implications of such technology are immense, and will vary from place to place. In a lot of jurisdictions, the laws with regards to facial recognition technology and the use of personal data remain in flux, hence the gray areas which an app like this occupies.
Data Protection Law: Many countries have strict laws regarding data protection, the General Data Protection Regulation or GDPR, applicable to the European Union, for example requires explicit consent before using personal data. Possibly, this app is not subject to such law.
Bans on facial recognition: There are ever-growing restrictions being placed on the use of facial recognition technology in public spaces. For example, San Francisco outlawed government agencies using facial recognition technology. Restrictions placed on such bans may also restrict the use of apps that rely on facial recognition.
Potential Legal Backlash: Should users feel their personal information has been infringed upon, they may possibly sue the developers, Meta, or anyone associated with rolling this app out.
Possible Benefits
In spite of an extreme reaction in criticism against the application, some possible benefits must be noted. Under regulated and consensual circumstances, this technology can prove to be highly useful:
The app would allow exhibition attendees to quickly access information relevant to the contacts they make during professional events or conferences. It should, therefore, be extremely useful for networking and even potentially significant conversations.
Customer Service: Employees operating in industries that are heavily dependent on personal service, such as hospitality or retail, use the app to receive fundamental facts about customers and thus are able to offer a highly individualized experience.
Safety Applications: The technology could, at some instances be used for security to allow law enforcement or security personal to trace persons of interest promptly.
Key Words / Phrases to Use When Optimizing this Blog
When optimizing this blog for search engines, here are important keywords and phrases to include:
Meta smart glasses app
Harvard students develop smart glasses app
Smart glasses privacy concerns
Augmented reality facial recognition
AR app reveals personal details
Ethical concerns with smart glasses
Data privacy in augmented reality
Facial recognition technology
Smart glasses legal implications
Meta AR privacy issues
Conclusion
The smart glasses app created by Harvard students is a precise example of how fast the world is changing and how knotty the questions of ethics and privacy around it are becoming. While this app promised great things with AR capabilities and facial recognition capabilities, it raised the question of a greater need for regulating aspects to protect the individual’s private space of the digital age.
The more augmented reality and facial recognition take hold, the more society will be asked to square technological advance with individual rights. This app reminds us of the fantastic benefits and grave dangers involved when the boundaries of what is possible are pushed in tech.
It has only just begun to talk around privacy and augmented reality, and responses now are going to dictate what that future is.
In a glance, these smart glasses will have all the details about every person the wearer may cross. Sounds like some sci-fi nonsense, but this technology is too real, and the fantastic innovation that presents so much great and risk has already entered public discourse with its attendant risks.
How Does It Work?
This app functions as an integrated combination of AI and machine learning combined with publicly available data. Here is a very condensed explanation of how the technology works:
Facial recognition: The smart glasses contain cameras that scan all the faces around the user. Using facial recognition software, the app can match those faces with images on social media sites or online.
Data aggregation: Whenever a person is identified through the application, it retrieves publicly available information of that person by aggregating from other online sources like social media profiles, professional profiles on LinkedIn, and so on.
Data Overlay in Real-Time: This data will be overlaid in real-time on the screen of the user’s smart glasses. This may include, among other things, name, job, interests, or even more sensitive information as far as it is available in the public domain.
The Privacy and Ethical Concerns
The technology behind the app is undoubtedly marvelous, but there are some serious concerns regarding privacy and ethics. It does bring up several pretty critical questions concerning consent and the right to privacy in public spaces-the concept of access to personal details about strangers instantly.
Lack of Consent
The most serious concern is that individuals going for scans will not control their information being disclosed. Generally, explicit consent must be obtained before information about people is released to the public or on public view. This gives rise to the fundamental issues of how people’s information will be used and if people have rights to opt out of information exposure.
Security Risks
The app would reveal all its sensitive information to the public, making it a tool for malicious actors. For example, if some person’s contact or location details are provided without their consent, they may end up being harassed or stalked. Identity theft, security breaches, and other risks may also come about from this data falling into the wrong hands.
Ethical Issues
Although the legal issues present themselves first, they are accompanied by wider moral questions surrounding surveillance and the intimacy of private information. Data privacy has long been the greatest subject of controversy; this app blurs lines between public information and private information, thus motivating a review of how much of our personal data should be offered to other people and even strangers without our knowledge and consent.
Legal Implications
The legal implications of such technology are immense, and will vary from place to place. In a lot of jurisdictions, the laws with regards to facial recognition technology and the use of personal data remain in flux, hence the gray areas which an app like this occupies.
Data Protection Law: Many countries have strict laws regarding data protection, the General Data Protection Regulation or GDPR, applicable to the European Union, for example requires explicit consent before using personal data. Possibly, this app is not subject to such law.
Bans on facial recognition: There are ever-growing restrictions being placed on the use of facial recognition technology in public spaces. For example, San Francisco outlawed government agencies using facial recognition technology. Restrictions placed on such bans may also restrict the use of apps that rely on facial recognition.
Potential Legal Backlash: Should users feel their personal information has been infringed upon, they may possibly sue the developers, Meta, or anyone associated with rolling this app out.
Possible Benefits
In spite of an extreme reaction in criticism against the application, some possible benefits must be noted. Under regulated and consensual circumstances, this technology can prove to be highly useful:
The app would allow exhibition attendees to quickly access information relevant to the contacts they make during professional events or conferences. It should, therefore, be extremely useful for networking and even potentially significant conversations.
Customer Service: Employees operating in industries that are heavily dependent on personal service, such as hospitality or retail, use the app to receive fundamental facts about customers and thus are able to offer a highly individualized experience.
Safety Applications: The technology could, at some instances be used for security to allow law enforcement or security personal to trace persons of interest promptly.
Key Words / Phrases to Use When Optimizing this Blog
When optimizing this blog for search engines, here are important keywords and phrases to include:
Meta smart glasses app
Harvard students develop smart glasses app
Smart glasses privacy concerns
Augmented reality facial recognition
AR app reveals personal details
Ethical concerns with smart glasses
Data privacy in augmented reality
Facial recognition technology
Smart glasses legal implications
Meta AR privacy issues
Conclusion
The smart glasses app created by Harvard students is a precise example of how fast the world is changing and how knotty the questions of ethics and privacy around it are becoming. While this app promised great things with AR capabilities and facial recognition capabilities, it raised the question of a greater need for regulating aspects to protect the individual’s private space of the digital age.
The more augmented reality and facial recognition take hold, the more society will be asked to square technological advance with individual rights. This app reminds us of the fantastic benefits and grave dangers involved when the boundaries of what is possible are pushed in tech.
It has only just begun to talk around privacy and augmented reality, and responses now are going to dictate what that future is.